|
|
7 months ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_types.h | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_util.c | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_util.h | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_validate.c | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_validate.h | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_verify.c | 7 months ago | |
| avb_aftl_verify.h | 7 months ago | |
| avb_ops_aftl.h | 7 months ago | |
| libavb_aftl.h | 7 months ago | |
README.md
Android Firmware Transparency Log 1.0
This repository contains tools and libraries for working with the Android Firmware Transparency Log components of Android Verified Boot. AFTL will be used to refer to these components.
[TOC]
What is it?
The Android Firmware Transparency Log (AFTL) is an implementation of binary transparency that leverages cryptographic proofs of inclusion of build images using a public append-only ledger. The device manufacturer stores these cryptographic proofs, called inclusion proofs, on-device to allow for offline validation of the build during system update and device boot. This ensures that only a publicly known build is running on the device. Furthermore, it allows device manufacturers and other interested parties to audit the information in the log to detect unexpected or malicious uses of the publisher's signing keys.
System overview
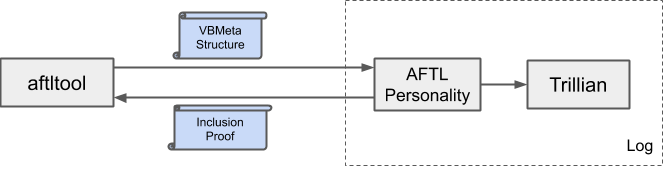
An AFTL can be implemented using a Trillian instance which manages a Merkle tree with build metadata (particularly the VBMeta struct) and keeps a repository of other data that were made transparent.
As part of the finalizing step in the build process the aftltool reaches out
to the AFTL personality to submit a manufacturer-signed message (containing
VBMeta struct and other metadata) to the AFTL. Then the AFTL personality
submits that data to Trillian to incorporate it into the Merkle tree. After
integration into the log, the AFTL personality returns the inclusion proof back
to the aftltool, which in turn incorporates the inclusion proof with the
VBMeta image.
The AFTL uses two sets of keys for authentication and validation, the transparency log key and the manufacturer key.
- Transparency log key: Used by Trillian to sign inclusion proofs. The public key is embedded with the device for on-device for validation.
- Manufacturer key: Used by OEMs or other build providers to sign submissions sent to the log. This ensures that malicious entries posing as a valid OEM entry cannot be provided to the log. For the log to authenticate messages, the manufacturer key must be shared out-of-band with the AFTL prior to submission.
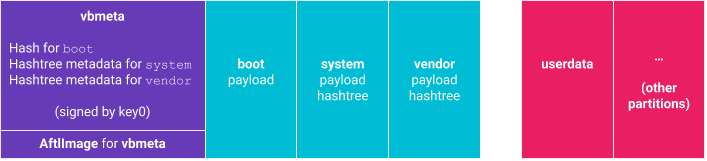
The AftlImage struct
The central data structure used for AFTL validation is the AftlImage struct.
The structure is saved on the vbmeta partition, right after the
AvbVBMetaImage struct, as illustrated below.
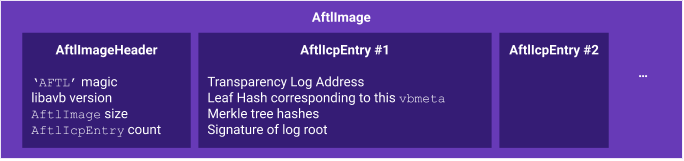
This structure contains the AftlImageHeader header that describes the number
of inclusion proofs (AftlIcpEntry) represented by this structure. Each
inclusion proof has associated metadata, such as the transparency log URL. A
high-level description of the structures is given below. See
aftltool
and
libavb_aftl
for more details.
Each AftlIcpEntry structure contains the information required to validate an
inclusion proof from a specific transparency log server for a given VBMeta
structure
given the corresponding transparency log public key. The inclusion proof
validation process is described in the inclusion proofs
section of this document.
Note: A single AftlImage can have multiple inclusion proofs from different
transparency logs. This allows the device manufacturer to not rely on a single
transparency log, and ensures that the builds represented by the VBMeta
structure are deemed transparent in multiple disparate jurisdictions.
Inclusion proofs
An inclusion proof allows a user to prove that a specific VBMeta structure is included in a transparency log. An inclusion proof consists of three parts:
- A
SignedVBMetaPrimaryAnnotationstructure containing the hash of the VBMeta structure (and other build meta information) that is signed with the manufacturer key. - A set of sibling node hashes (
Proof) in a Merkle tree on the path from the leaf node in question, which represents the logged annotation, to the root node. - A
TrillianLogRootDescriptorstructure containing the log's root hash, along with related metadata, which is signed by the transparency log’s private key.
Validation of an inclusion proof can be performed with the following steps,
which are implemented in both aftltool and libavb_aftl.
- Calculate the hash of the VBMeta structure stored on the device.
- Determine if the hash matches the hash stored in the
SignedVBMetaPrimaryAnnotationstructure inside theAftlImageon device. If it does, continue validation. - Given the set of hashes provided from the transparency log as part of the inclusion proof, attempt to recalculate the root hash. Details of the process can be found here in the Merkle Audit Proofs section.
- Check the calculated root hash against the log's root hash from the inclusion proof. If it matches, continue validation.
- Finally, verify the log root signature given the calculated root hash and the public key of the transparency log that is stored on device. If the signature is valid, the inclusion proof is valid.
Tools and libraries
This section contains information about the tools and libraries added to AVB repository or modified to include AFTL support.
aftltool and libavb_aftl
The main purpose of
aftltool
is to add an inclusion proof to an existing vbmeta.img to be used
for transparency checks at boot or system update time. This enhanced image is
stored in the vbmeta partition or in the vbmeta_a and
vbmeta_b slots when using A/B and will still be of minimal size
(for out-of-band updates). Creation, query, and verification tasks can be
performed with aftltool.
In addition to the aftltool, the
libavb
library comes with an extension called
libavb_aftl.
This component performs all verification on the device side related to AFTL and
inclusion proofs. That is, it loads the vbmeta partition, checks
the VBMeta structure signature, walks through each inclusion proof stored in
the AftlImage, and validates them against a trusted transparency
log key stored on the device.
This library is intended to be used in both the boot loader and inside Android
as part of the OTA client. The main entry point for verification is
aftl_slot_verify(), which is intended to be called after vbmeta
verification is done via avb_slot_verify().
Files and directories
libavb_aftl/- An implementation of AFTL inclusion proof validation. This
code is designed to be highly portable so it can be used in as many contexts
as possible. This code requires a C99-compliant C compiler. Only the content
declared in
libavb_aftl.his considered public. The other files are considered internal to the implementation and may change without notice.
- An implementation of AFTL inclusion proof validation. This
code is designed to be highly portable so it can be used in as many contexts
as possible. This code requires a C99-compliant C compiler. Only the content
declared in
libavb_aftl/README.md- This document.
test/- Unit tests for
libavb_aftl.
- Unit tests for
test/data/- Test data for the
aftltoolandlibavb_aftlunit tests.
- Test data for the
aftltool- A symlink to
aftltool.py.
- A symlink to
aftltool.py- A tool written in Python for working with images related to AFTL.
Android.bp- Build rules for
aftltool,libavb_aftl(a static library for use on the device), host-side libraries (for unit tests), and unit tests.
- Build rules for
aftltool_test.py- Source-code for
aftltoolrelated unit tests.
- Source-code for
aftltool_integration_test.py- Source-code for
aftltoolrelated integration tests against a live transparency log.
- Source-code for
Portability
The libavb_aftl code is intended to be used in bootloaders in devices that
will load Android or other operating systems. The suggested approach is to copy
the appropriate header and C files mentioned in the previous section into the
boot loader and integrate as appropriate. The library is intended to be highly
portable, working on both little and big endian architectures, as well as
32-bit and 64-bit variants of each. It is also intended to work in environments
without the standard C library and runtime.
As in libavb, if the AVB_ENABLE_DEBUG preprocessor symbol is set, the code
will include useful debug information and run-time checks.
Versioning and compatibility
The libavb_aftl library follows the versioning of
libavb.
Using aftltool
The content for the vbmeta partition is assumed to have been generated
previously using avbtool. Instructions can be found in the
README.md
for libavb. After the VBMeta partition is generated, it can be extended with
inclusion proofs from transparency logs in the following manner:
aftltool make_icp_from_vbmeta \
--vbmeta_image_path /path/to/image.bin \
--output OUTPUT \
[--signing_helper /path/to/external/signer] \
[--signing_helper_with_files /path/to/external/signer_with_files] \
--version_incremental STR \
--transparency_log_servers host:port,/path/to/log_key.pub \
--manufacturer_key /path/to/priv_key \
[--padding_size NUM]
The version_incremental is a part of the build fingerprint which allows for tagging the transparency log entry for easier tracking.
An example of how to use the make_icp_from_vbmeta command is as follows:
aftltool make_icp_from_vbmeta \
--vbmeta_image_path ./vbmeta.img \
--output ./vbmeta_icp.img \
--version_incremental 99999999 \
--transparency_log_servers \
log.aftl-android.com:9000,/aftl-log-rsa-pub.pem \
--manufacturer_key ./manufacturer-rsa.pem \
--algorithm SHA256_RSA4096 \
--padding 4096
The AFTL information can be viewed in a human readable format in the following manner:
aftltool info_image_icp \
--vbmeta_image_path /path/to/image.bin \
[--output OUTPUT]
An example using info_image_icp is as follows:
aftltool info_image_icp --vbmeta_image_path ./vbmeta.img
Verification of an AFTL enhanced vbmeta image can be performed with the following command:
aftltool verify_image_icp \
--vbmeta_image_path /path/to/image.bin \
--transparency_log_pub_keys [TRANSPARENCY_LOG_PUB_KEYS [TRANSPARENCY_LOG_PUB_KEYS ...]]
[--output OUTPUT]
An example using verify_image_icp is as follows:
aftltool verify_image_icp --vbmeta_image_path ./vbmeta.img --transparency_log_pub_keys ./log_pub_key.pem
More information on the options can be found using aftltool --help.
Build system integration
AFTL modifications only will work if AVB is enabled in the build. In Android,
AVB is enabled in an Android.mk file by the BOARD_AVB_ENABLE variable as
described in the AVB
README.md.
When calling the sign_target_files_apks.py script, the following parameters must be set:
--aftl_tool_path, the location of aftltool.py--aftl_server, the address of the transparency log--aftl_key_path, which gives the path to the DER encoded transparency log public key--aftl_manufacturer_key_path, which gives the path to the DER encoded OEM private key. Note: This key is different to the signing key used to sign VBMeta structure
Remember that the public part of the transparency log keys need to be available to the bootloader of the device to validate the inclusion proofs.
Device integration
This section discusses recommendations and best practices for integrating
libavb AFTL support with a device boot loader. It's important to emphasize
that these are just recommendations. Most of these recommendations are the same
as those for AVB.
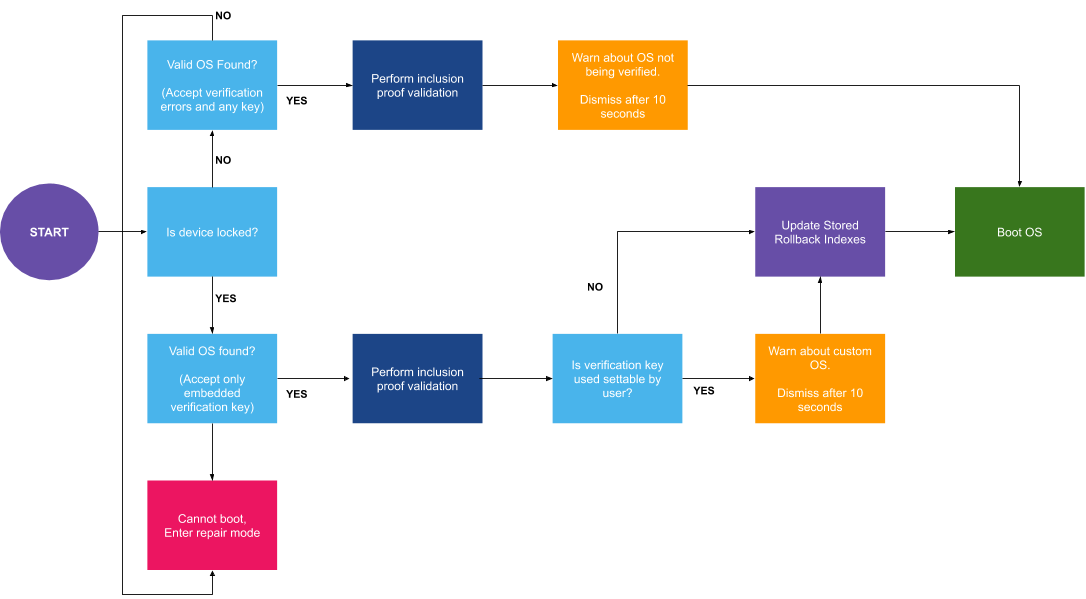
Recommended bootflow
The boot flow should ensure checking of the inclusion proofs independent of the unlock state of the device. It is recommended to present the user with a warning in case transparency checks fail.
AFTL modifies this flow in the following manner: as soon as a valid OS has been
found, search for an AftlImage for each VBMeta image and validate their
inclusion proofs (this is done by the aftl_slot_verify function). The result
of the verification can be appended to the kernel command line for further
processing by the OS.